Enantioselective Radical Hydrocyanoalkylation of Alkenes via Photoenzymatic Catalysis
Dongshan Wu,† Zeying Sun,† Sanshan Wang, Jun Yang, Jingyuan He, and Xiaoguang Lei*
JACS Au 2025, doi:10.1021/jacsau.5c00633
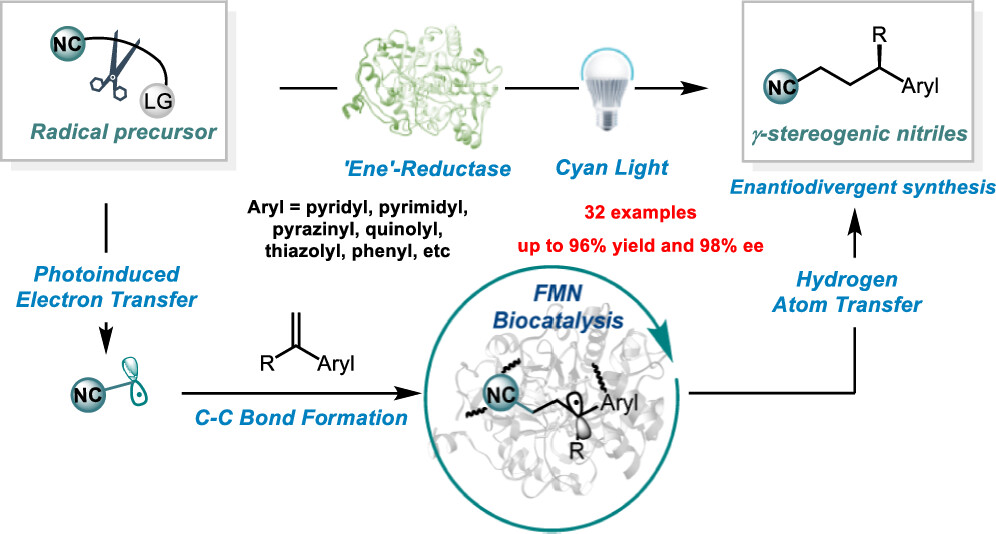
Organic nitriles are significant in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, cosmetics, and materials. Although numerous cyanidation methods have been developed, more eco-friendly and green protocols for manufacturing alkyl nitriles are in high demand. Here, we report a photoenzymatic enantioselective intermolecular hydrocyanoalkylation of alkenes catalyzed by flavin-dependent “ene”-reductases. The discovery of stereocomplementary enzymes that provide access to both enantiomers of the high-value nitriles further showcases the synthetic applications of this method. Radical trapping, isotopic labeling, and spectroscopic experiments have elucidated the formation of a charge transfer complex at the protein active site. The single-electron reduction of the cyanoalkyl radical precursor by flavin hydroquinone yields a cyanoalkyl radical, which then undergoes intermolecular radical addition. This active site can stereoselectively control the radical-terminating hydrogen atom transfer, enabling the synthesis of enantioenriched γ-stereogenic nitriles. This work further expands the reactivity repertoire of biocatalytic transformations via non-natural radical mechanisms.