Quotes
在科学上没有平坦的大道,只有那些不畏艰险沿着陡峭山路攀登的人,才有希望达到光辉的顶点。
----马克思
-----------------------------------------------
Research Projects
Collaborations
请有兴趣的研究组联系我们。欢迎任何形式的合作,尤其是在自组装、水凝胶以及生物医药等方向的合作。
------------------------------------------
Publications
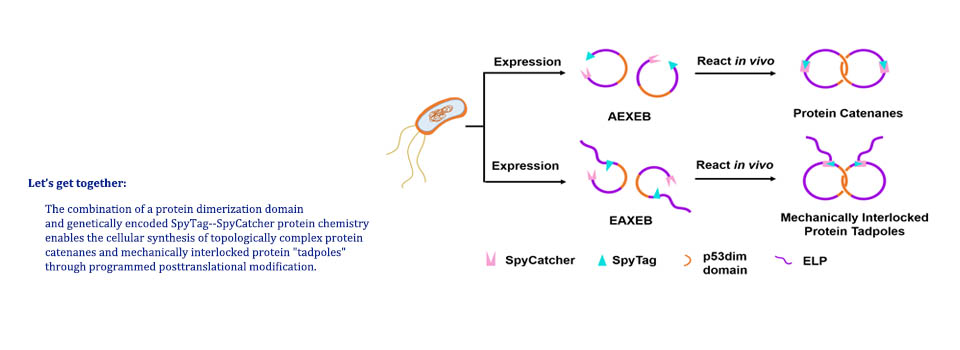
Yin, G.; Wei, J.; Shao, Y.; Wu, W.-H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.-B.* Native Conjugation between Proteins and [60]Fullerene Derivatives using SpyTag as a Reactive Handle, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, DOI: /doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.04.034.
Abstract: Herein, we report the facile conjugation between proteins and water-soluble [60]fullerene derivatives under native conditions using SpyTag as a reactive handle. Water-soluble [60]fullerene derivatives (DC60) were first prepared via sequential Bingel-Hirsch reaction and “clicked” with SpyTag to give DC60-SpyTag for native conjugation with proteins by the highly efficient SpyTag-SpyCatcher chemistry. The bioconjugation was confirmed by MALDI-TOF MS spectra and SDS-PAGE analysis. The TEM and UV-vis spectroscopic study further revealed that the DC60 could alter the optical performance and induce aggregation of the target proteins. It thus provides a general and robust method for modifying proteins with C60 derivatives and could potentially be adapted for native conjugation between proteins and other nonbiological motifs as well.