Research Summary
1、We present an antibody-free, FTO-assisted chemical labeling method termed m6A-SEAL for specific m6A detection
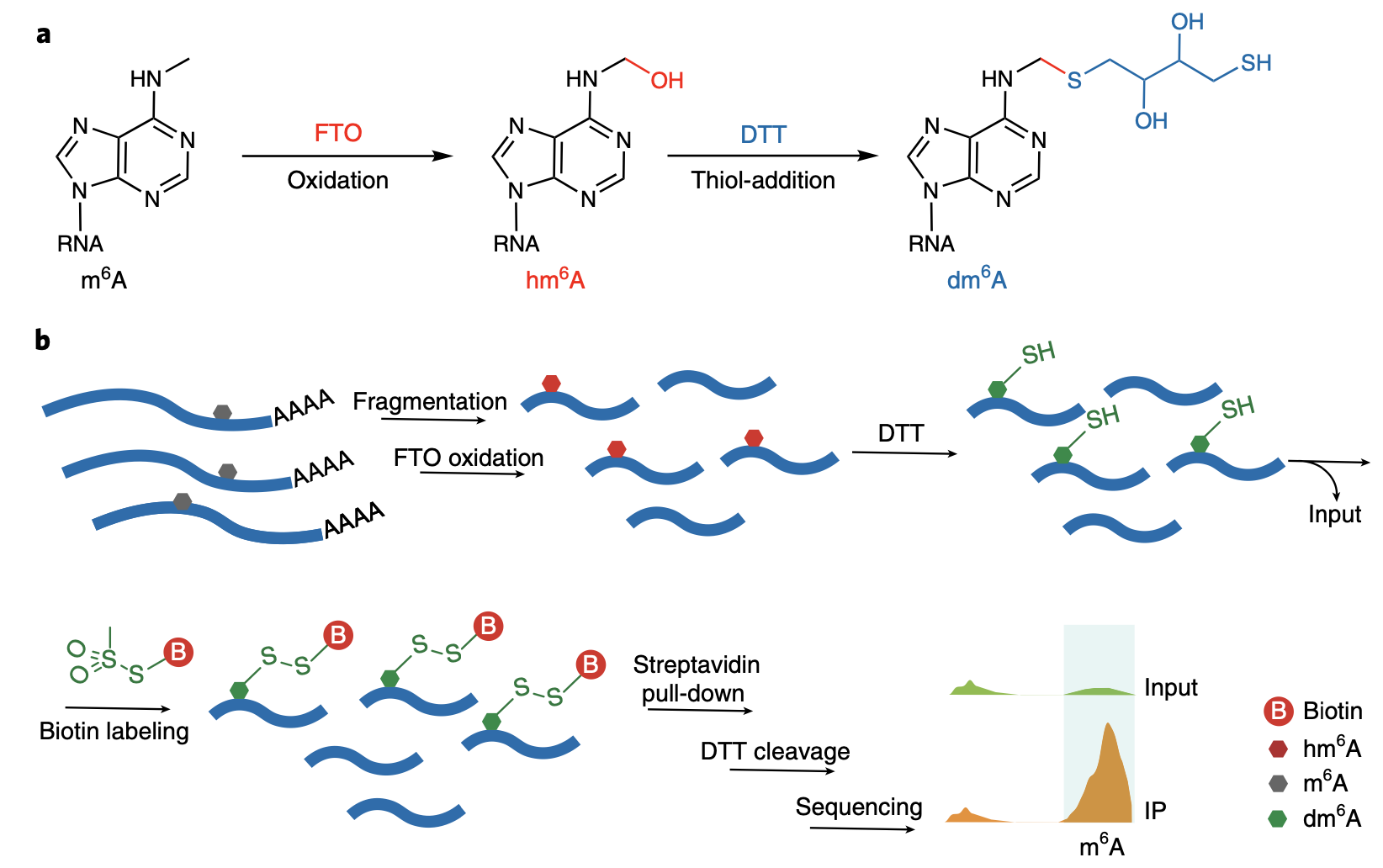
The inert chemical property of RNA modification N6-methyladenosine (m6A) makes it very challenging to detect. Most m6A sequencing methods rely on m6A-antibody immunoprecipitation and cannot distinguish m6A and N6,2′-O-dimethyladenosine modification at the cap +1 position (cap m6Am). Although the two antibody-free methods (m6A-REF-seq/MAZTER-seq and DART-seq) have been developed recently, they are dependent on m6A sequence or cellular transfection. Here, we present an antibody-free, FTO-assisted chemical labeling method termed m6A-SEAL for specific m6A detection. We applied m6A-SEAL to profile m6A landscapes in humans and plants, which displayed the known m6A distribution features in transcriptome. By doing a comparison with all available m6A sequencing methods and specific m6A sites validation by SELECT, we demonstrated that m6A-SEAL has good sensitivity, specificity and reliability for transcriptome-wide detection of m6A. Given its tagging ability and FTO’s oxidation property, m6A-SEAL enables many applications such as enrichment, imaging and sequencing to drive future functional studies of m6A and other modifications.
2、We show that transgenic expression of the human RNA demethylase FTO in rice caused a more than threefold increase in grain yield under greenhouse conditions.

RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications are essential in plants. Here, we show that transgenic expression of the human RNA demethylase FTO in rice caused a more than threefold increase in grain yield under greenhouse conditions. In field trials, transgenic expression of FTO in rice and potato caused ~50% increases in yield and biomass. We demonstrate that the presence of FTO stimulates root meristem cell proliferation and tiller bud formation and promotes photosynthetic efficiency and drought tolerance but has no effect on mature cell size, shoot meristem cell proliferation, root diameter, plant height or ploidy. FTO mediates substantial m6A demethylation (around 7% of demethylation in poly(A) RNA and around 35% decrease of m6A in non-ribosomal nuclear RNA) in plant RNA, inducing chromatin openness and transcriptional activation. Therefore, modulation of plant RNA m6A methylation is a promising strategy to dramatically improve plant growth and crop yield.

