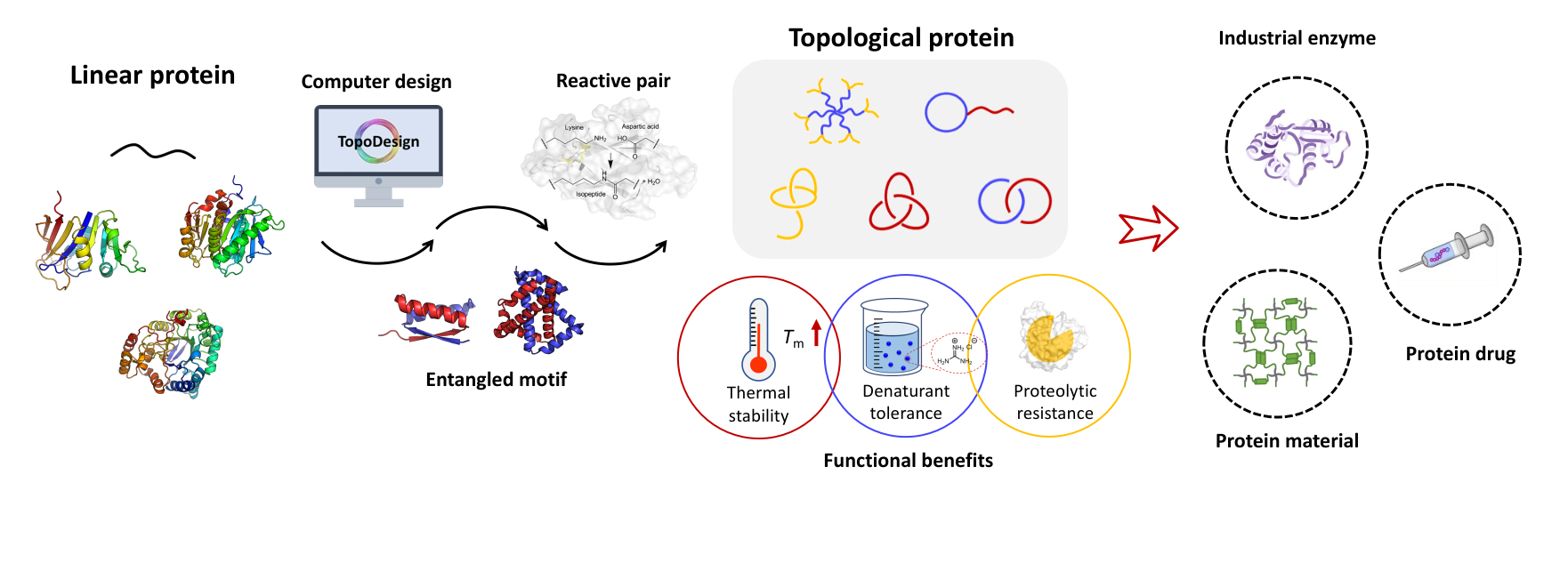
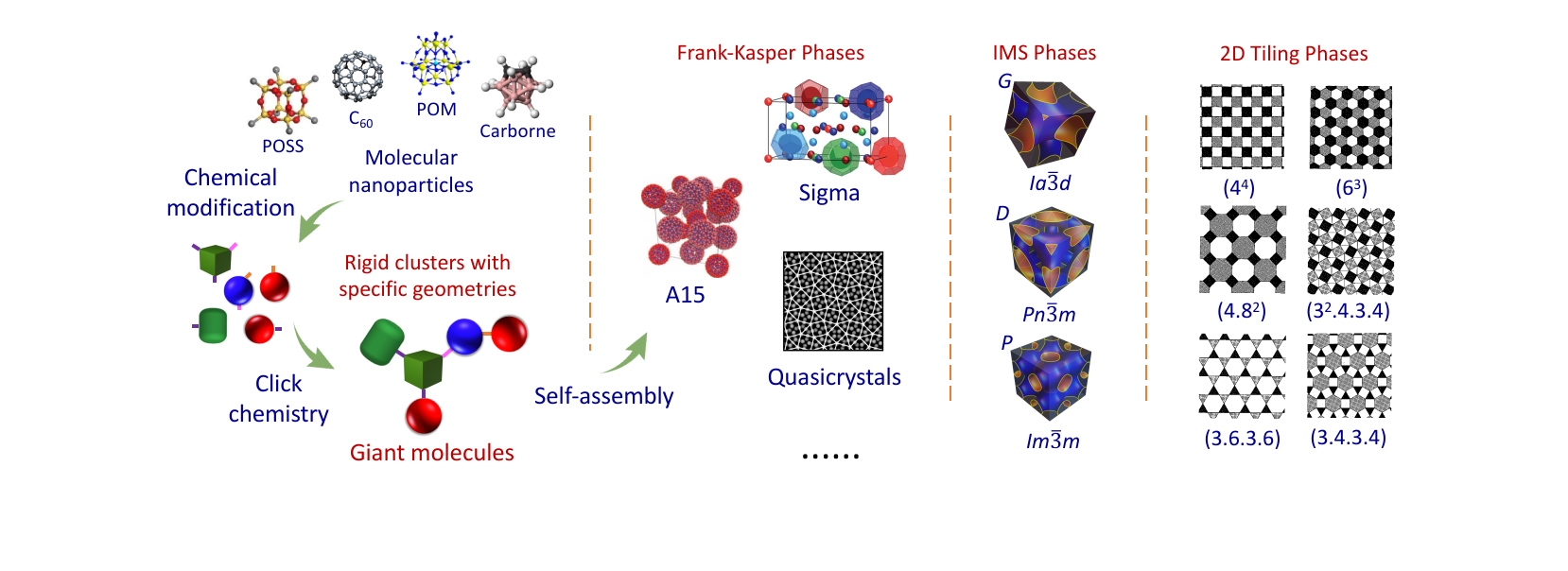
最新热点
联系我们
张文彬课题组
地址:北京市海淀区成府路202号
北京大学化学与分子工程学院
邮编:100871
电话:010-62766876
电邮:wenbin@pku.edu.cn

请扫以上二维码关注我们课题组的公众号。
我们将定期推送组会每周精读和泛读文献介绍以及课题组的最近新闻!
--------------------------------------------
最新成果
Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.-H.; Peng, R.; Zhang, W.-B.* A Moonlighting Superpositively Charged SpyCatcher. CCS Chem. 2023, DOI: 10.31635/ccschem.023.202202620. https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.023.202202620

Genetically encoded covalent peptide tagging tools such as the SpyTag/SpyCatcher reactive pair, have been demonstrated versatile and useful for protein modification. Herein, we present a superpositively charged SpyCatcher bearing a theoretical net charge of +21 capable of accomplishing multiple unrelated independent tasks to enrich this toolbox and cultivate new functions. The SpyCatcher(+21) possessed stimuli-responsive reactivity toward SpyTag and could serve as a potent and general platform for the delivery of proteins, including RNase A into HeLa cells. Remarkably, the delivered RNase A caused substantial proliferation inhibition toward HeLa cells. In addition, the superpositively charged SpyCatcher could form coacervate with plasmid DNA for further study of gene delivery and liquid–liquid phase separation. These findings demonstrate the robustness of the SpyTag/SpyCatcher structure against surface mutation and the prospect of applying supercharging technology on diverse functional proteins to create moonlighting proteins.