研究室工作进展 May. 5th, 2019
The functionalization of white phosphorus (P4) through direct P−C bond formation has been a continuous interest because of the chlorine-free synthesis of organophosphorus compounds. Since the first report of P−C bond formation by reaction of organolithium with P4 in 1963, continuous efforts have been made in order to convert P4 into organophosphorus compounds directly. Although the conversions of P4 to various [MxPy]n complexes have gained great achievements, the direct formation of organophosphorus compounds from P4 are rare. In fact, making organophosphorus compounds through direct P−C bond formation from P4 generally suffers from: i) high electrophilic reactivity of the P4 tetrahedron, ii) the low selectivity for the P−P bond rupture after the first P−P bond cleavage, and iii) the low conversion efficiency of the phosphorus atoms in P4. Thus, the controllable and atom-efficient functionalization of P4 to construct directly organophosphorus or polyphosphorus compounds is highly desirable.
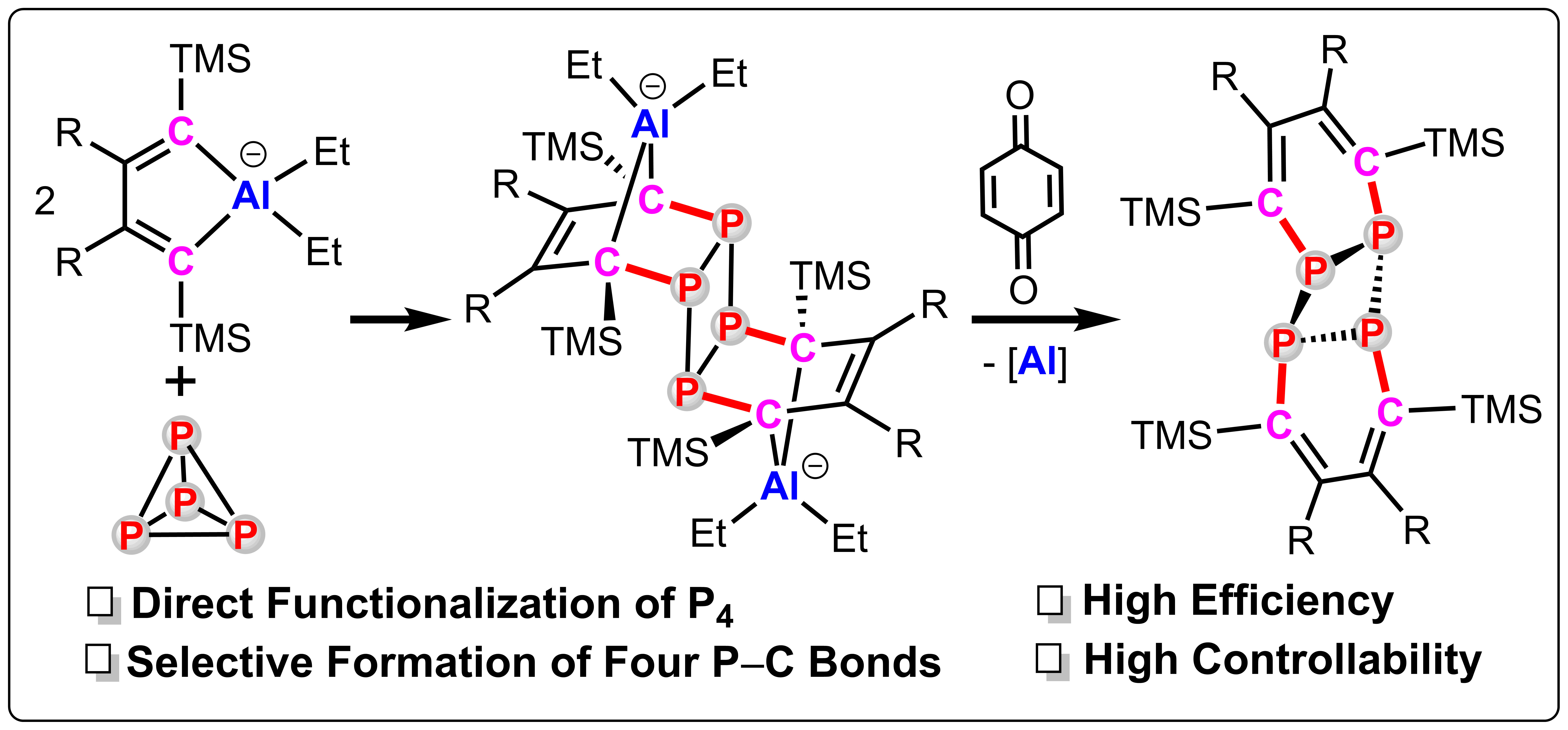
The ate-complexes of aluminacyclopentadienes react with P4 selectively affording the cyclotetraphosphanes featuring four newly formed P−C bonds and a planar square cyclo-P4 ring. DFT calculations show that the conversion of tetrahedral P4 to planar cyclo-P4 moiety undergoes through an unexpected 1,1-P-insertion/D-A reaction/isomerization cascade process. The reaction of these complexes with iodomethane or p-benzoquinone can afford the P-methylation product and the metal-free cyclotetraphosphane, respectively. This work shows a promising synthetic route to the cyclotetraphosphanes starting from P4 and throws a light on the functionalization of P4 to organophosphorus compounds.
亮点介绍
白磷活化直接合成有机膦化合物具有十分重要的科学意义,该过程避免了工业合成中常用的PCl3等剧毒化合物以及产生的废酸等污染问题。近三十年来,白磷活化的研究一直被人们所关注并取得了一些进展。但到目前为止,该研究领域仍然存在许多挑战性问题:1)反应选择性低,产物不可控;2)合成有机膦的效率低且研究匮乏;3)机理研究匮乏;4)f区金属活化白磷的研究匮乏。因此,由白磷直接高效、高选择性地合成有机膦化合物就十分重要与必要。
2016年,我们利用丁二烯基桥联的双锂试剂与白磷直接反应,在温和的条件下,首次实现了从白磷直接高效高选择性合成磷杂环戊二烯基锂的方法(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9187–9190.)。2017年,我们利用稀土金属杂环戊二烯同时作为双亲核试剂与双烯体试剂,通过白磷的[3+1]-碎片化反应,分离和表征了磷杂环戊二烯基锂和第一例稀土金属cyclo-P3化合物(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15886–15890.)。2018年,我们详细研究了磷杂戊二烯基锂的固体聚集态结构,其可以为单体、二聚体、配位聚合物等多种形式(Organometallics 2018, 37, 2018–2022.)。2019年,我们分离并表征了四种磷锂簇合物,其分别为Li3(THF)6P7、Li4(THF)10P14、Li2(THF)6P16和Li4(THF)13P26(Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 71–75.)。
最近,我们研究了铝杂环戊二烯促进的白磷活化。铝杂环戊二烯与白磷反应可以高选择性、高收率地得到含铝的cyclo-P4化合物,其同时构建了四根P−C键,具有一个规整的平面正方形cyclo-P4结构。理论计算表明该反应经历了一个1,1-P-插入、D−A反应、异构化的串联反应机理。该化合物与碘甲烷反应可以得到P-甲基化的季鏻盐化合物,与对苯醌反应可以得到不含金属的四磷杂环丁烷衍生物。这是目前合成四磷杂环丁烷最高效的方法,也为白磷活化直接合成有机膦化合物提供了一种新思路。
