
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
您的位置:首页 > 研究方向
|
|
|
|
|
方向一 液晶高分子分子设计、合成与性能研究:液晶高分子的分子设计、合成及性能研究。 最新研究进展: |
| Hierarchical Structures in a Main-Chain/Side-Chain Combined Liquid Crystalline Polymer with a Polynorbornene Backbone and Multi-Benzene Side-Chain Mesogens Ping-Ping Hou, Zhen-Yu Zhang, Qian Wang, Meng-Yao Zhang, Zhihao Shen, and Xing-He Fan Macromolecules 2016, 49(19), 7238-7245. |
|
A series of main-chain/side-chain combined liquid crystalline polymers (MCSCLCPs) with a polynorbornene backbone and multi-benzene mesogens in the side chain, PNbnPP (n = 2, 6, 10), were synthesized through a controllable polymerization method: ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP). Differential scanning |
| Hierarchically Self-Assembled Amphiphilic Alternating Copolymer Brush Containing Side-Chain Cholesteryl Units Jing Ping, Kehua Gu, Sheng Zhou, Hongbing Pan, Zhihao Shen, and Xing-He Fan Macromolecules 2016, 49(16), 5993-6000. |
|
|
| Synthesis and Characterization of New Liquid Crystalline Thermoplastic Elastomers Containing Mesogen-Jacketed Liquid Crystalline Polymers Zhen-Yu Zhang, Qi-Kai Zhang, Zhihao Shen, Jian-Peng Yu, Yi-Xian Wu, and Xing-He Fan Macromolecules 2016, 49(2), 475-482. |
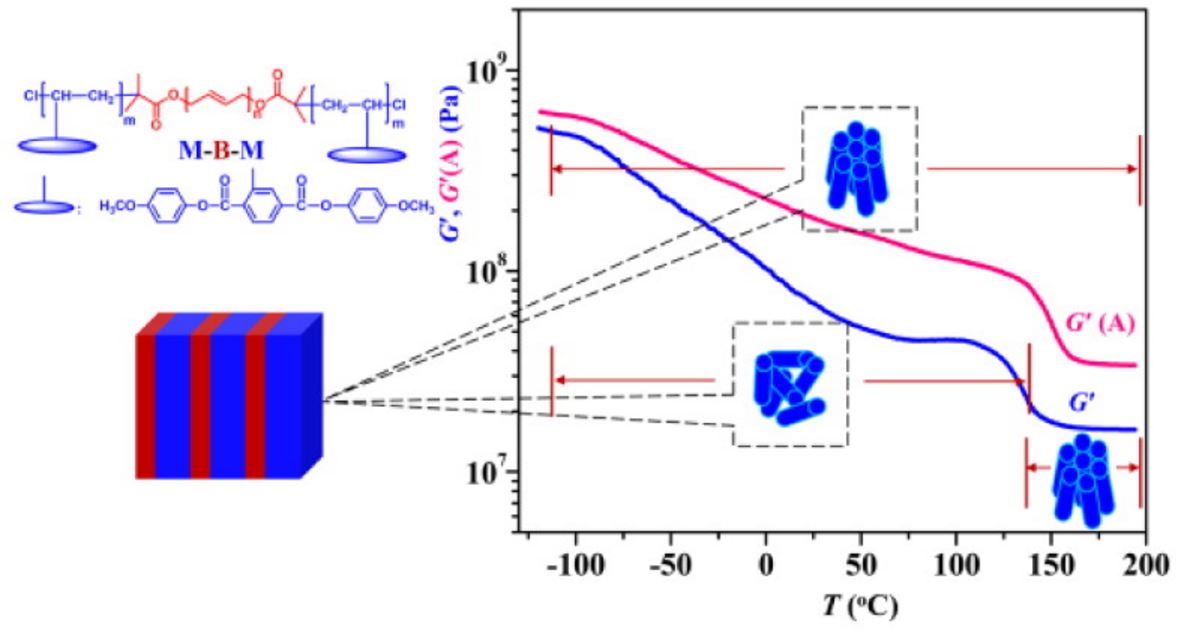 In order to improve the high-temperature performance of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), we designed and synthesized a new kind of ABA triblock copolymer containing a mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymer (MJLCP), poly{2,5-bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)oxycarbonyl]styrene} (PMPCS), as the hard blocks and polybutadiene (PB) as the soft block. The triblock copolymer, PMPCS-b-PB-b-PMPCS (M-B-M), was synthesized by ring-opening metathesis polymerization in the presence of a chain In order to improve the high-temperature performance of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), we designed and synthesized a new kind of ABA triblock copolymer containing a mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymer (MJLCP), poly{2,5-bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)oxycarbonyl]styrene} (PMPCS), as the hard blocks and polybutadiene (PB) as the soft block. The triblock copolymer, PMPCS-b-PB-b-PMPCS (M-B-M), was synthesized by ring-opening metathesis polymerization in the presence of a chaintransfer agent and atom transfer radical polymerization. The glass transition temperature (Tg) of the PMPCS hard block is 110?118 °C in the triblock copolymers. In addition, the liquid crystalline (LC) phase of PMPCS is stable before thermal decomposition. All the triblock copolymers form lamellar microphase-separated structures, as demonstrated by small-angle X-ray scattering and transmission electron microscopy results. The triblock copolymer (M-B-M-55) with a mass fraction of 55% of PMPCS exhibits typical properties of an LC thermoplastic elastomer (LCTPE). The maximum elongation at break and the tensile strength of M-B-M-55 are 736% and 10.6 MPa, respectively, and the stretching strength at 300% is 6.9 MPa. Above the Tg of PMPCS, the LC phase of PMPCS provides new physical cross-linking points in the LCTPEs, and the triblock copolymer M-B-M-55 still shows a relatively high modulus. |
| Effects of rigid cores and flexible tails on the phase behaviors of polynorbornene-based mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymer Zhen-Yu Zhang, Qian Wang, Ping-Ping Hou, Zhihao Shen and Xing-He Fan Polymer Chemistry 2015, 6(44), 7701-7710. |
|
A new series of mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymers (MJLCPs) with a polynorbornene main chain and different side groups were prepared by ring-opening metathesis polymerization. The liquid crystalline (LC) phase behaviors of these polymers were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry, polarized light microscopy, and wide-angle X-ray diffraction. Depending on the rigid side-chain core and peripheral alkyl chains, these polymers show different LC structures. The polymer with the terphenyl rigid side-chain core and relatively short alkyl tails is amorphous in the whole temperature range, while those with the same rigid side-chain core but longer alkyl tails exhibit columnar nematic (Coln) phases. Polymers |
| Synthesis and Properties of a Coil-g-Rod Polymer Brush by Combination of ATRP and Alternating Copolymerization Jing Ping, Yangyang Qiao, Haijian Tian, Zhihao Shen, Xinghe Fan Macromolecules 2015, 48(3), 592-599. |
|
|
| Mesogen-Jacketed Liquid Crystalline Polymers with a Polynorbornene Main Chain: Green Synthesis and Phase Behaviors Yufeng Zhu, Zhenyu Zhang, Qikai Zhang, Pingping Hou, Dezhao Hao, Yangyang Qiao , Zhihao Shen, Xinghe Fan, and Qifeng Zhou Macromolecules 2014, 47(9), 2803-2810. |
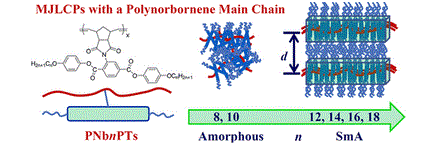 We synthesized a new series of MJLCPs with a polynorbornene main chain, PNbnPT (n = 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, which is the number of carbons in the side-chain alkyl tails), through ring-opening metathesis polymerization and investigated their phase behaviors. The monomers were facilely synthesized in satisfactory yields through a key intermediate, N-(2,5-dicarboxylphenyl)-cis-5-norbornene-exo-2,3-dicarboximide. Differential scanning calorimetry, polarized light microscopy, and wide-angle X-ray diffraction results demonstrate that the phase behavior of PNbnPT is strongly dependent on the alkyl-tail length. Polymers with relatively short alkyl tails, PNb8PT and PNb10PT, are amorphous in the whole temperature range before degradation. When the alkyl-tail length increases, PNbnPTs (n = 12, 14, 16, 18) develop into the smectic A phase, and the degree of order increases with increasing alkyl-tail length. The synthetic pathway for MJLCPs with a polynorbornene main chain in this work is more robust and greener than those reported to the best of our knowledge. And MJLCPs with a polynorbornene main chain show quite different phase behaviors compared with those with a polyethylene backbone, and they may be used to create fascinating functional materials. We synthesized a new series of MJLCPs with a polynorbornene main chain, PNbnPT (n = 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, which is the number of carbons in the side-chain alkyl tails), through ring-opening metathesis polymerization and investigated their phase behaviors. The monomers were facilely synthesized in satisfactory yields through a key intermediate, N-(2,5-dicarboxylphenyl)-cis-5-norbornene-exo-2,3-dicarboximide. Differential scanning calorimetry, polarized light microscopy, and wide-angle X-ray diffraction results demonstrate that the phase behavior of PNbnPT is strongly dependent on the alkyl-tail length. Polymers with relatively short alkyl tails, PNb8PT and PNb10PT, are amorphous in the whole temperature range before degradation. When the alkyl-tail length increases, PNbnPTs (n = 12, 14, 16, 18) develop into the smectic A phase, and the degree of order increases with increasing alkyl-tail length. The synthetic pathway for MJLCPs with a polynorbornene main chain in this work is more robust and greener than those reported to the best of our knowledge. And MJLCPs with a polynorbornene main chain show quite different phase behaviors compared with those with a polyethylene backbone, and they may be used to create fascinating functional materials. |
| Synthesis and phase behavior of a new 2-vinylbiphenyl-based mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymer with a high glass transition temperature and low threshold molecular weight Qikai Zhang, Haijian Tian, Changfeng Li, Yufeng Zhu, Yongri Liang, Zhihao Shen and Xinghe Fan Polymer Chemistry 2014, 5(15), 4526-4533. |
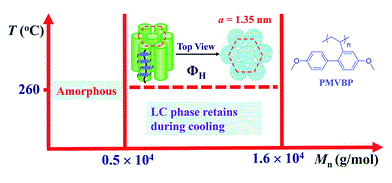 We have synthesized a new mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymer, poly(4′-(methoxy)-2-vinylbiphenyl-4-methyl ether) (PMVBP) containing a biphenyl core in the side-chain. PMVBP has a smaller monomer molecular weight (MW), a higher glass transition temperature and a lower threshold MW for liquid crystalline (LC) formation. PMVBP was obtained via a nitroxide-mediated living radical polymerization and characterized by gel permeation chromatography, differential scanning calorimetry, polarized light microscopy, and one- and two-dimensional wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) experiments. The number-average MW (Mn) of the polymers ranges from 0.41 × 104 to 1.64 × 104 g mol-1. A relatively high glass transition temperature is observed, which increases from 173 to 208 °C with increasing MW. The LC phase developed at relatively high temperatures is strongly dependent on the Mn of the polymer. A hexagonal columnar (ΦH) LC phase is observed above 260 °C when the Mn is only above 0.53 × 104 g mol -1, a low threshold MW for LC formation. All of the LC phases are retained during cooling. We have synthesized a new mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymer, poly(4′-(methoxy)-2-vinylbiphenyl-4-methyl ether) (PMVBP) containing a biphenyl core in the side-chain. PMVBP has a smaller monomer molecular weight (MW), a higher glass transition temperature and a lower threshold MW for liquid crystalline (LC) formation. PMVBP was obtained via a nitroxide-mediated living radical polymerization and characterized by gel permeation chromatography, differential scanning calorimetry, polarized light microscopy, and one- and two-dimensional wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) experiments. The number-average MW (Mn) of the polymers ranges from 0.41 × 104 to 1.64 × 104 g mol-1. A relatively high glass transition temperature is observed, which increases from 173 to 208 °C with increasing MW. The LC phase developed at relatively high temperatures is strongly dependent on the Mn of the polymer. A hexagonal columnar (ΦH) LC phase is observed above 260 °C when the Mn is only above 0.53 × 104 g mol -1, a low threshold MW for LC formation. All of the LC phases are retained during cooling. |
| Competition and Promotion between Two Different Liquid Crystalline Building Blocks: Mesogen-Jacketed Liquid Crystalline Polymers and Triphenylene Discotic Liquid Crystals Yufeng Zhu , Xiaolin Guan , Zhihao Shen, Xinghe Fan, and Qifeng Zhou Macromolecules 2012, 45(8), 3346-3355. |
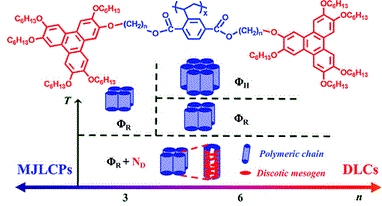 Mesogen-jacketed liquid-crystalline polymers (MJLCPs) containing two triphenylene (Tp) units in the side chains, denoted as PPnV (n = 3 or 6, which is the number of the methylene units between the terephthalate core and Tp moieties in the side chains), were synthesized through conventional free radical polymerization, and the phase behaviors of these new combined main-chain/side-chain liquid-crystalline (LC) polymers were investigated. The chemical structures of the monomers were confirmed by elemental analysis, high-resolution mass spectrometry, and 1H/13C NMR. The molecular characterizations of the polymers were performed with 1H NMR, gel permeation chromatography, and thermogravimetric analysis. LC behaviors of the polymers were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarized light microscopy, and wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD). Both polymers exhibit excellent thermal stabilities. DSC and WAXD results indicate that covalently incorporating Tp discotic liquid crystals has a tremendous effect on the LC behaviors of MJLCPs. As expected, the glass-transition temperature decreases as the spacer length increases. Both polymers form rectangular columnar (ΦR) phases at relatively high temperatures. At low temperatures, however, Tp moieties in the side chains form a discotic nematic (ND) phase in conjunction with the ΦR phase developed by the rod-like supramolecular mesogen – the MJLCP chain as a whole, owing to the self-organization of the Tp moieties. For PP6V in particular, a higher symmetry hexagonal columnar (ΦH) phase forms when temperature exceeds 225 °C. Individual ordered structures developed by these two LC building blocks are not only competitive but also promotive to each other. Mesogen-jacketed liquid-crystalline polymers (MJLCPs) containing two triphenylene (Tp) units in the side chains, denoted as PPnV (n = 3 or 6, which is the number of the methylene units between the terephthalate core and Tp moieties in the side chains), were synthesized through conventional free radical polymerization, and the phase behaviors of these new combined main-chain/side-chain liquid-crystalline (LC) polymers were investigated. The chemical structures of the monomers were confirmed by elemental analysis, high-resolution mass spectrometry, and 1H/13C NMR. The molecular characterizations of the polymers were performed with 1H NMR, gel permeation chromatography, and thermogravimetric analysis. LC behaviors of the polymers were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarized light microscopy, and wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD). Both polymers exhibit excellent thermal stabilities. DSC and WAXD results indicate that covalently incorporating Tp discotic liquid crystals has a tremendous effect on the LC behaviors of MJLCPs. As expected, the glass-transition temperature decreases as the spacer length increases. Both polymers form rectangular columnar (ΦR) phases at relatively high temperatures. At low temperatures, however, Tp moieties in the side chains form a discotic nematic (ND) phase in conjunction with the ΦR phase developed by the rod-like supramolecular mesogen – the MJLCP chain as a whole, owing to the self-organization of the Tp moieties. For PP6V in particular, a higher symmetry hexagonal columnar (ΦH) phase forms when temperature exceeds 225 °C. Individual ordered structures developed by these two LC building blocks are not only competitive but also promotive to each other. |
|
方向二 高分子复杂体系多层次多尺度相结构、相转变及动力学:含液晶高分子链段的嵌段共聚物的自组装等。 最新研究进展: |
|
| Thermoreversible Ion Gel with Tunable Modulus Self-Assembled by a Liquid Crystalline Triblock Copolymer in Ionic Liquid Yudong Zhang, Xinghe Fan, Zhihao Shen, and Qifeng Zhou Macromolecules 2015, 48(14), 4927-4935. |
|
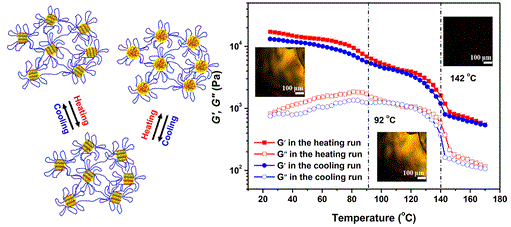 Ion gels with tunable storage moduli are prepared through the self-assembly of an ABAtriblock copolymer AOA-12 comprised of a thermotropic liquid crystalline (LC) polymer as the end-block A and poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) as the mid-block B in a room-temperatureionic liquid (IL), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsufonyl)imide ([EMIM][TFSI]). The PEO mid-block is well-solvated by this ionic liquid, whereas the LC polymer end-blocks aggregate and serve as the physical cross-linkers. For comparison, a triblock copolymerAOA-0 containing a non-LC side-chain polymer with the same mesogen is also synthesized, and its corresponding ion gel is prepared. The ion gels with relatively high concentrations of the LC triblock copolymer have hierarchical structures with different microphase-separated nanostructures and the LC arrangement of the LC blocks. By incorporating the azobenzene mesogen in the side chains, transparent AOA-n/[EMIM][TFSI] (where n is the number of carbon atoms in the spacer between the azobenzene mesogen and the polymethacrylate backbone, and n = 0, 12), ion gels are obtained with concentrations of the polymer as low as around 2 wt %. The ion gel obtained has a storage modulus as high as ~10 kPa, while its conductivity is close to that of the pure IL mainly because of the high IL concentration of theion gel. Furthermore, the storage modulus of the AOA-12/IL ion gel can be tuned by temperature because of the thermotropic phase behavior of the LC block. These ion gels are potentially useful as high-temperature ionic membranes or thermal-responsive soft actuators. Ion gels with tunable storage moduli are prepared through the self-assembly of an ABAtriblock copolymer AOA-12 comprised of a thermotropic liquid crystalline (LC) polymer as the end-block A and poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) as the mid-block B in a room-temperatureionic liquid (IL), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsufonyl)imide ([EMIM][TFSI]). The PEO mid-block is well-solvated by this ionic liquid, whereas the LC polymer end-blocks aggregate and serve as the physical cross-linkers. For comparison, a triblock copolymerAOA-0 containing a non-LC side-chain polymer with the same mesogen is also synthesized, and its corresponding ion gel is prepared. The ion gels with relatively high concentrations of the LC triblock copolymer have hierarchical structures with different microphase-separated nanostructures and the LC arrangement of the LC blocks. By incorporating the azobenzene mesogen in the side chains, transparent AOA-n/[EMIM][TFSI] (where n is the number of carbon atoms in the spacer between the azobenzene mesogen and the polymethacrylate backbone, and n = 0, 12), ion gels are obtained with concentrations of the polymer as low as around 2 wt %. The ion gel obtained has a storage modulus as high as ~10 kPa, while its conductivity is close to that of the pure IL mainly because of the high IL concentration of theion gel. Furthermore, the storage modulus of the AOA-12/IL ion gel can be tuned by temperature because of the thermotropic phase behavior of the LC block. These ion gels are potentially useful as high-temperature ionic membranes or thermal-responsive soft actuators. |
|
| Synthesis and Self-Assembly of Rod-Rod Block Copolymers with Different Rod Diameters Feng Zhou, Tieying Ye, Lingying Shi, Chan Xie, Shankui Chang, Xinghe Fan, and Zhihao Shen Macromolecules 2013, 46(20), 8253-8263. |
|
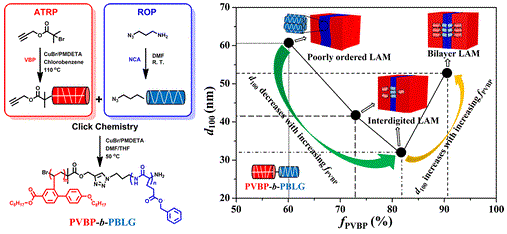 We synthesized a series of rod–rod block copolymers, poly(octyl-4′-(octyloxy)-2-vinylbiphenyl-4-carboxylate)-b-poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate) (PVBP-b-PBLG) with different rod diameters, and we focused on the effect of size disparity on their self-assembling behaviors in bulk. By using differential scanning calorimetry, wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD), small-angle X-ray scattering, and transmission electron microscopy techniques, we found that the columnar nematic (ΦN) liquid crystalline phase of PVBP and the hexagonal columnar (ΦH) phase of PBLG were disrupted to different extents depending on the volume fractions of PVBP (fPVBP’s). When fPVBP is about 60%, the ΦH phase of PBLG is retained with the appearance of the two second-order diffractions in WAXD patterns. When fPVBP is increased to above 73%, the ordered structure of PBLG is destroyed, and when fPVBP is 91% even the first-order diffraction peak disappears. At the same time, the ΦN phase of PVBP changes from poorly ordered to well ordered with increasing fPVBP. Accordingly, with fPVBP increasing from 60% to 91%, the microphase-separated structure goes through a poorly ordered structure to an interdigitated lamellar morphology and to a bilayer lamellar structure. We synthesized a series of rod–rod block copolymers, poly(octyl-4′-(octyloxy)-2-vinylbiphenyl-4-carboxylate)-b-poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate) (PVBP-b-PBLG) with different rod diameters, and we focused on the effect of size disparity on their self-assembling behaviors in bulk. By using differential scanning calorimetry, wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD), small-angle X-ray scattering, and transmission electron microscopy techniques, we found that the columnar nematic (ΦN) liquid crystalline phase of PVBP and the hexagonal columnar (ΦH) phase of PBLG were disrupted to different extents depending on the volume fractions of PVBP (fPVBP’s). When fPVBP is about 60%, the ΦH phase of PBLG is retained with the appearance of the two second-order diffractions in WAXD patterns. When fPVBP is increased to above 73%, the ordered structure of PBLG is destroyed, and when fPVBP is 91% even the first-order diffraction peak disappears. At the same time, the ΦN phase of PVBP changes from poorly ordered to well ordered with increasing fPVBP. Accordingly, with fPVBP increasing from 60% to 91%, the microphase-separated structure goes through a poorly ordered structure to an interdigitated lamellar morphology and to a bilayer lamellar structure. |
|
| Remarkably Rich Variety of Nanostructures and Order–Order Transitions in a Rod–Coil Diblock Copolymer Ling-Ying Shi, Yu Zhou, Xinghe Fan, and Zhihao Shen Macromolecules 2013, 46(13), 5308-5316. |
|
|
|
|
| Solvent-Induced Hierarchical Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic PEG(Gm)-b-PS Dendritic-Linear Block Copolymers Huanhuan Cai, Guoliang Jiang, Zhihao Shen, and Xinghe Fan Soft Matter 2013, 9(47), 11398-11404. |
|
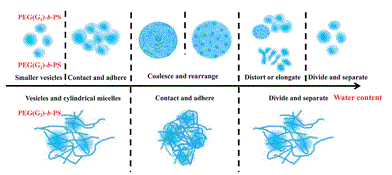 The self-assembly of dendritic-linear block copolymers PEG(Gm)-b-PS (where m?is the generation number, and m = 1, 2, 3) of different generations with similar hydrophilic weight fractions in aqueous media was studied. With the increasing generation number, the self-assembled aggregates transform from polydisperse vesicles to a mixture of cylindrical micelles with a few vesicles. Turbidity measurements, transmission electron microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy were used to explore the effect of the solvent on the aggregation process in mixtures of tetrahydrofuran–water. Depending on the content of water added, many intermediate structures like large compound vesicles with porous surfaces or combined morphologies from vesicles and cylindrical micelles could be found. In situ?monitoring of the intermediate structures provided mechanistic insights regarding their formation processes. For PEG(G1)-b-PS and PEG(G2)-b-PS, the results showed that the fusion and fission processes occur during the addition of water. The fusion process is composed of two steps. First, the vesicles contact and adhere to each other. Second, they rearrange to form larger structures. In the fission process, the large structures are distorted or elongated at first, and then they transform into smaller vesicles. For PEG(G3)-b-PS, only the adhesion and separation processes were detected, without further fusion and fission. Comparing the aggregation processes induced by solvent of samples with different dendron generations, we propose that it is easy for the fusion process to take place between vesicles and difficult between vesicles and cylindrical micelles. The self-assembly of dendritic-linear block copolymers PEG(Gm)-b-PS (where m?is the generation number, and m = 1, 2, 3) of different generations with similar hydrophilic weight fractions in aqueous media was studied. With the increasing generation number, the self-assembled aggregates transform from polydisperse vesicles to a mixture of cylindrical micelles with a few vesicles. Turbidity measurements, transmission electron microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy were used to explore the effect of the solvent on the aggregation process in mixtures of tetrahydrofuran–water. Depending on the content of water added, many intermediate structures like large compound vesicles with porous surfaces or combined morphologies from vesicles and cylindrical micelles could be found. In situ?monitoring of the intermediate structures provided mechanistic insights regarding their formation processes. For PEG(G1)-b-PS and PEG(G2)-b-PS, the results showed that the fusion and fission processes occur during the addition of water. The fusion process is composed of two steps. First, the vesicles contact and adhere to each other. Second, they rearrange to form larger structures. In the fission process, the large structures are distorted or elongated at first, and then they transform into smaller vesicles. For PEG(G3)-b-PS, only the adhesion and separation processes were detected, without further fusion and fission. Comparing the aggregation processes induced by solvent of samples with different dendron generations, we propose that it is easy for the fusion process to take place between vesicles and difficult between vesicles and cylindrical micelles. |
|
|
方向三 光电高分子材料分子设计、合成和性能研究:光电高分子材料分子设计、合成和性能研究。 最新研究进展: |
| Synthesis and Characterization of Electrophosphorescent Jacketed Conjugated Polymers Wei Zhang, Hao Jin, Feng Zhou, Zhihao Shen, Dechun Zou and Xinghe Fan Journal of Polymer Science Part A-Polymer Chemistry 2012, 50(18), 3895-3903. |
|
|
| Dendron-Jacketed Electrophosphorescent Copolymers: Improved Efficiency and Tunable Emission Color by Partial Energy Transfer Hao Jin, Wei Zhang, Dan Wang, Zengze Chu, Zhihao Shen, Dechun Zou, Xinghe Fan, and Qifeng Zhou Macromolecules 2011, 44(24), 9556-9564. |
|
|
| Synthesis and Properties of Dendritic Emitters with a Fluorinated Starburst Oxadiazole Core and Twisted Carbazole Dendrons Zhenhua Zhao, Hao Jin, Yanxin Zhang, Zhihao Shen, De-Chun Zou, and Xinghe Fan Macromolecules 2011, 44(6), 1405-1413. |
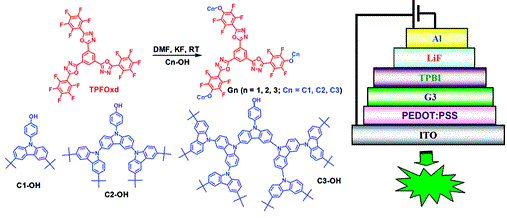 Three generations of novel dendrimers (G1, G2, and G3) with an electron-deficient fluorinated starburst oxadiazole core and twisted carbazoles as dendrons were synthesized via aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction at ambient temperature by the weak base potassium fluoride with a high selectivity in a nearly quantitative yield, which was attributed to the high reactivity of the para fluorine atom activated by oxadiazole and multiple fluorine atoms. 1H NMR, 19F NMR, elemental analysis, and MALDI-TOF MS results confirmed the designed chemical structures. Varying the generation to gradually modify the dendrons could gradiently modulate the HOMO-LUMO energy band gaps of Gn, which was verified by cyclic voltammetry results. Photoluminescent spectra showed the dual fluorescence emission of the dendrimers in solutions, which indicated that twist intramolecular charge transfer occurred between oxadiazole and carbazole separated by nonconjugated bonds. The Gn-based devices with the configuration of ITO/PEDOT:PSS/Gn/TPBI/AlQ/LiF/Al displayed a stable green emission in their electroluminescent spectra with a gradual increase in external quantum efficiency and current efficiency for higher-generation dendrimers, owing to gradually improved charge transport. The device with G3 possessed the lowest turn-on voltage along with the highest external quantum efficiency of 1.49%, maximum current efficiency of 4.6 cd/A, and a high luminance of 4882 cd/m2, indicating that it had the best carrier balance. Three generations of novel dendrimers (G1, G2, and G3) with an electron-deficient fluorinated starburst oxadiazole core and twisted carbazoles as dendrons were synthesized via aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction at ambient temperature by the weak base potassium fluoride with a high selectivity in a nearly quantitative yield, which was attributed to the high reactivity of the para fluorine atom activated by oxadiazole and multiple fluorine atoms. 1H NMR, 19F NMR, elemental analysis, and MALDI-TOF MS results confirmed the designed chemical structures. Varying the generation to gradually modify the dendrons could gradiently modulate the HOMO-LUMO energy band gaps of Gn, which was verified by cyclic voltammetry results. Photoluminescent spectra showed the dual fluorescence emission of the dendrimers in solutions, which indicated that twist intramolecular charge transfer occurred between oxadiazole and carbazole separated by nonconjugated bonds. The Gn-based devices with the configuration of ITO/PEDOT:PSS/Gn/TPBI/AlQ/LiF/Al displayed a stable green emission in their electroluminescent spectra with a gradual increase in external quantum efficiency and current efficiency for higher-generation dendrimers, owing to gradually improved charge transport. The device with G3 possessed the lowest turn-on voltage along with the highest external quantum efficiency of 1.49%, maximum current efficiency of 4.6 cd/A, and a high luminance of 4882 cd/m2, indicating that it had the best carrier balance. |
|
方向四 多组分高分子体系、有机-无机杂化体系的分子设计、合成和性能研究:共混物等。 最新研究进展: |
| POSS-Containing Jacketed Polymer: Hybrid Inclusion Complex with Hierarchically Ordered Structures at Sub-10 nm and Angstrom Length Scales Yufeng Zhu, Wei Liu, Mengyao Zhang, Yu Zhou, Yudong Zhang, Pingping Hou, Yu Pan, Zhihao Shen, Xinghe Fan and Qifeng Zhou Macromolecules 2015, 48(8), 2358-2366. |
|
|
| Ordered Gold Nanoparticle Arrays Obtained with Supramolecular Block Copolymers Tieying Ye, Xiaofang Chen, Xinghe Fan and Zhihao Shen Soft Matter 2013, 9(18), 4715-4724. |
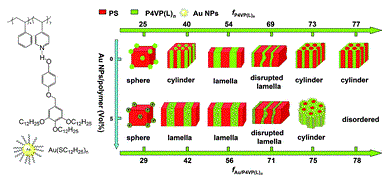 We demonstrate a simple approach to produce self-assembly of nanocomposites of gold nanoparticles with a supramolecular block copolymer formed by a fan-shaped small molecule L and polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinyl pyridine) (PS-b-P4VP) through hydrogen bonding. Hybrids PS-b-P4VP(L)n, where n is the molar ratio of L to 4VP, were obtained by blending the polymer PS-b-P4VP, the small molecule L, and gold nanoparticles. With the use of the supramolecular approach, chemical modification of either the nanoparticle or the polymer is unnecessary. The organization of Au nanoparticles with controlled inter-particle distance and ordering was realized by changing the value of n. In addition, a hierarchical structure-within-structure morphology was observed for one of the hybrids, Au/PS-b-P4VP(L)1.0, in which the Au/P4VP(L)n domains form a hexagonal packing stabilized by nano-phase separation. The hybrids self-assemble into sphere, lamella, or cylinder structures, which were characterized by small-angle X-ray scattering and transmission electron microscopy. The contents of both L and Au NPs can affect the type and size of the self-assembled structure. We demonstrate a simple approach to produce self-assembly of nanocomposites of gold nanoparticles with a supramolecular block copolymer formed by a fan-shaped small molecule L and polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinyl pyridine) (PS-b-P4VP) through hydrogen bonding. Hybrids PS-b-P4VP(L)n, where n is the molar ratio of L to 4VP, were obtained by blending the polymer PS-b-P4VP, the small molecule L, and gold nanoparticles. With the use of the supramolecular approach, chemical modification of either the nanoparticle or the polymer is unnecessary. The organization of Au nanoparticles with controlled inter-particle distance and ordering was realized by changing the value of n. In addition, a hierarchical structure-within-structure morphology was observed for one of the hybrids, Au/PS-b-P4VP(L)1.0, in which the Au/P4VP(L)n domains form a hexagonal packing stabilized by nano-phase separation. The hybrids self-assemble into sphere, lamella, or cylinder structures, which were characterized by small-angle X-ray scattering and transmission electron microscopy. The contents of both L and Au NPs can affect the type and size of the self-assembled structure. |
|
方向五 形状两性分子的合成、自组装及性质研究:有机-无机杂化材料等。 最新研究进展: |
|
| The synthesis and self-assembly of disc-cube dyads with spacers of different lengths Meng-Yao Zhang, Ke-Hua Gu, Yu Zhou, Sheng Zhou, Xing-He Fan and Zhihao Shen Chemical communications 2016, 52(20), 3923-3926. |
|
|
Disc-cube dyads with a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) molecule covalently attached to a hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene (HBC) molecule were designed and synthesized. The results demonstrate that the length of a spacer plays an important role in the selfassembly behavior of the HBC–POSS dyad. |
|
|
方向六 特种高性能聚合物分子设计、合成及其复合材料研究:以国家重要技术需求为主导,从聚合物合成化学的核心和源头进行创新,开展以耐高温聚合物材料为基础组分的多相体系聚合物和高性能及功能化材料的制备等有关聚合物复合材料新技术的基础和应用研究。在此基础上,开发高性能、多功能聚合物复合材料的制备技术。 最新研究进展: |
|
| Synthesis, Preparation and Properties of Novel High-Performance Allyl-Maleimide Resins Haoyu Tang, Wanwan Li, Xinghe Fan, Xiaofang Chen, Zhihao Shen, Qifeng Zhou Polymer 2009, 50(6), 1414-1422. |
|
, 1414-1422.jpg) Three novel allyl–maleimide monomers (i.e., A2B, AB and AB2) were designed, synthesized and thermally cured to yield a series of high-performance allyl–maleimide resins. Of the thermal stability of the cured allyl–maleimide resins (i.e., PA2B, PAB and PAB2), PA2B and PAB2 showed good glass transition temperatures and their corresponding composites showed high bending modulus. Allyl-compound-modified BMI resins based on AB monomer were prepared. The processability of the prepolymer (BR–AB-pre) was improved by the addition of AB monomer. The cured BMI resins (BR and BR–AB) showed good thermal stability, high glass transition temperature, and good mechanical properties and low water uptake. Three novel allyl–maleimide monomers (i.e., A2B, AB and AB2) were designed, synthesized and thermally cured to yield a series of high-performance allyl–maleimide resins. Of the thermal stability of the cured allyl–maleimide resins (i.e., PA2B, PAB and PAB2), PA2B and PAB2 showed good glass transition temperatures and their corresponding composites showed high bending modulus. Allyl-compound-modified BMI resins based on AB monomer were prepared. The processability of the prepolymer (BR–AB-pre) was improved by the addition of AB monomer. The cured BMI resins (BR and BR–AB) showed good thermal stability, high glass transition temperature, and good mechanical properties and low water uptake. |
|
| Crosslinkable Poly(aryl ether ketone)s Containing Pendant Phenylethynyl Moieties: Synthesis, Characterization and Properties Wanwan Li, Haoyu Tang, Xaiofang Chen, Xinghe Fan, Zhihao Shen, Qifeng Zhou Polymer 2008, 49(19), 4080-4086. |
|
, 4080-4086.jpg) A novel phenylethynyl-contained bisphenol monomer, (2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)(4-(2-phenylethynyl)-phenyl)methanone (PEBP), has been synthesized and characterized. The resultant monomer was copolymerized with hydroquinone and 4,40-difluorobenzophenone by means of an aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction to provide a series of crosslinkable poly(aryl ether ketone)s containing pendant phenylethynyl moieties (PE-PAEKs). The solubility of PE-PAEKs tended to be improved with the increase in PEBP content. Wide-angle X-ray diffraction results showed that introduction of bulky pendant groups into molecular chains led to decrease in crystallinity. PE-PAEKs were successfully cured upon heating. Dynamic mechanical analysis results indicated that the glass-transition temperature of the cured PE-PAEKs was increased. Thermogravimetric analysis results implied that the thermal stability of the cured PE-PAEKs was excellent. A novel phenylethynyl-contained bisphenol monomer, (2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)(4-(2-phenylethynyl)-phenyl)methanone (PEBP), has been synthesized and characterized. The resultant monomer was copolymerized with hydroquinone and 4,40-difluorobenzophenone by means of an aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction to provide a series of crosslinkable poly(aryl ether ketone)s containing pendant phenylethynyl moieties (PE-PAEKs). The solubility of PE-PAEKs tended to be improved with the increase in PEBP content. Wide-angle X-ray diffraction results showed that introduction of bulky pendant groups into molecular chains led to decrease in crystallinity. PE-PAEKs were successfully cured upon heating. Dynamic mechanical analysis results indicated that the glass-transition temperature of the cured PE-PAEKs was increased. Thermogravimetric analysis results implied that the thermal stability of the cured PE-PAEKs was excellent. |
|
Copyright © 2016 | 周其凤研究组 | 地址:北京大学化学学院(北京市海淀区成府路292号) 北京 100871 | 联系我们